When you are invited to play a game, you most likely will want to follow the rules, in order to gain something from playing - whether it is winning a price like getting your diploma, or something else we perceive having value, like being accepted by your peers and other people. This certainly is socially intelligent behaviour, but how much does it really relate to the cognitive part of intelligence: the physiological effectiveness of out neural system in storing and retrieving data from the brain and the ways of knowing? Or understanding our own values and being willing and able to negotiate with those who have conflicting views?
IQ testing is an attempt to measure operational intelligence. The component behind our cognitive skills (language/math skills, logical reasoning, spatial sense, etc) is called the general intelligence factor. While I do recall going through reading speed testing at school, I never got the impression that intelligence would have been overly emphasized during my schooling. The message was more along the lines that everyone can learn and that we should engage in dialogue to better understand each other.
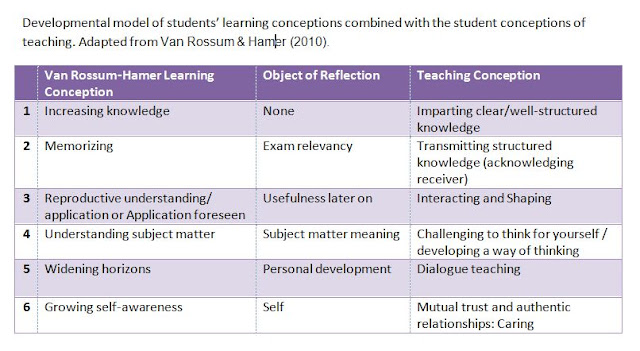
So, what about the meaning-oriented learning, and the intelligence that is much harder to measure by standardized IQ test? My own thinking about intelligence and learning is growing along the lines of the adult development and life-long learning, and I think that reproductive learning orientation is not sufficient.
Van Rossum & Hamer have a fascinating book "The Meaning of Learning and Knowing" that has influenced my thinking about how we learn.
Learning as understanding the connections between different theories or models is the way I see broad/general intelligence to be used best. This type of learning includes challenges and problem solving, but also requires lots of collaborative meaning-making and learner agency being a central part of each individual journey.
I think I am a lifelong learner -- there is so much to lean, and so little time to do it!
wfe2
Drago-Severson, E. (2004). Becoming adult learners: Principles and practices for effective development. Teachers College Press.
Kegan, R. (2009). What” form” transforms. A constructive-developmental approach to transformative learning. Teoksessa K. Illeris (toim.) Contemporary theories of learning: learning theorists in their own words. Abingdon: Routledge, 35-54.
Van Rossum, E. J., &
Hamer, R. N. (2010). The meaning of learning and knowing. Sense Publishers.